Buriram province
This article is written like a travel guide. (November 2014) |
Buriram
บุรีรัมย์ (Thai) มฺืงแปะ (Northern Khmer) | |
|---|---|
| Buriram province | |
Clockwise from top: Phanom Rung Historical Park, Chang Arena, Khao Kradong Forest Park, Romburi Park, Lam Nang Rong Dam, Prasat Muang Tam | |
| Motto(s): เมืองปราสาทหิน ถิ่นภูเขาไฟ ผ้าไหมสวย รวยวัฒนธรรม เลิศล้ำเมืองกีฬา ("Town of stone castles. Land of volcanos. Beautiful silk. Rich in culture. Superb sports city") | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Buriram province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Buriram |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Piya Pijnam (since December 2024) |
| Area | |
• Total | 10,080 km2 (3,890 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 17th |
| Population (2019)[2] | |
• Total | 1,595,747 |
| • Rank | Ranked 6th |
| • Density | 159/km2 (410/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 24th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2022) | 0.6136 "low" Ranked 72nd |
| GDP | |
| • Total | baht 84 billion (US$2.7 billion) (2019) |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 31xxx |
| Calling code | 044 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-31 |
| Vehicle registration | บุรีรัมย์ |
| Website | buriram.go.th |
Buriram province (Thai: จังหวัดบุรีรัมย์, RTGS: Changwat Buri Ram, pronounced [tɕāŋ.wàt bū.rīː.rām]) is one of Thailand's seventy-seven Provinces (changwat) and lies in lower northeastern Thailand, also called Isan. Neighboring provinces are (from south clockwise) Sa Kaeo, Nakhon Ratchasima, Khon Kaen, Maha Sarakham, and Surin. The name "Buriram" means 'city of happiness'.
Geography
[edit]
Buriram is at the south end of the Khorat Plateau, with several extinct volcanoes around the province. The southern limit of the province is a mountainous area at the limit between the Sankamphaeng Range and the Dângrêk Mountains. The total forest area is 887 km2 (342 sq mi) or 8.8 percent of provincial area.[1]
National park
[edit]There is one national park, along with three other national parks, make up region 1 (Prachinburi) of Thailand's protected areas.
- Ta Phraya National Park, 594 km2 (229 sq mi)[5]: 82
Wildlife sanctuary
[edit]There is one wildlife sanctuary, along with two other wildlife sanctuaries, make up region 7 (Nakhon Ratchasima) of Thailand's protected areas.
- Dong Yai Wildlife Sanctuary, 313 km2 (121 sq mi)[6]: 3
History
[edit]
The study of archaeologists has found evidence of human habitation since prehistoric times in Dvaravati period in Buriram including cultural evidence from the ancient Khmer Empire, which has both a brick castle and more than 60 stone castles, and have found important archaeological sites, including kilns, pottery and pottery, earthenware called Khmer wares, which determines the age around the 15th-18th. After the period of ancient Khmer or Khmer culture, the historical evidence of Buriram began to appear again at the end of the Ayutthaya period, which appears to be an old city and later appeared in the Thonburi period to the Rattanakosin period that Buriram was a city.
About a thousand years ago, the area that makes up today's Buriram Province was under the Khmer Empire and many ruins remain from that time. The largest, standing on an extinct volcano, is in the Phanom Rung Historical Park. According to an inscription found there, its local ruler recognised the authority of the Khmer king. However, the area was remote and sparsely populated, and little is recorded about it until the Rattanakosin Kingdom. In the early-19th century, Muang Pae, the largest town, acknowledged Thai sovereignty and was renamed Buriram. Following administrative reforms in the late-19th century, Buriram was formally incorporated into Thailand as a province with its own governor.
Culture
[edit]Festivals
[edit]Aside from important religious days, Songkran Day and New Year's Day, Buriram also has other local festivals such as the festival of the 5th lunar month[7] when the locals make merit, bathe Buddha images and the aged, play traditional sports such as Saba and tug of war. In some areas like Phutthaisong District, there is the Bang Fai traditional rocket dance, Khao Phansa, at the beginning of Buddhist Lent and Loi Krathong.
Demographics
[edit]Buriram is one of the northeastern provinces with a sizable Northern Khmer population. The Isan language is spoken by most, but according to the most recent census 27.6% of the population also speak Northern Khmer in everyday life.
Symbols
[edit]

The provincial seal depicts Phanom Rung temple, a Khmer-style Hindu shrine dedicated to Shiva. It was in use from the 9th through the 12th centuries, when the Khmer Empire's control of the region was ended by the Thais of Ayutthaya Kingdom. The ruins are now preserved in a historical park.
The provincial flower is the yellow cotton tree (Cochlospermum regium). The provincial tree is the pink shower (Cassia grandis). The Asian glass shrimp (Macrobrachium lanchesteri) is the provincial aquatic animal.
The province's motto is "the city of sandstone sanctuaries, land of volcanoes, beautiful silk, rich culture and the best city of sport".
Administrative divisions
[edit]
Provincial government
[edit]The province is divided into 23 districts (amphoes). The districts are further divided into 189 subdistricts (tambons) and 2,212 villages (mubans).
Local government
[edit]As of 26 November 2019 there are:[8] one Buriram Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 62 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Buriram, Chum Het and Nang Rong have town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 59 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 146 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[2]
Transport
[edit]Airports
[edit]Buriram Airport is the only airport in Buriram province. Two airlines, Nok Air and Thai AirAsia, serve Buriram from Don Mueang International Airport (DMK).

Highways
[edit]- Highway 218: Buriram - Nang Rong
- Highway 219: Ban Kruat - Prakhon Chai - Buriram - Ban Dan - Satuek - Phayakkhaphum Phisai - Yang Sisurat - Na Chueak - Borabue
- Highway 226: Nakhon Ratchasima - Chaloem Phra Kiat - Chakkarat - Huai Thalaeng - Lam Plai Mat - Buriram - Krasang - Surin - Sikhoraphum - Samrong Thap - Huai Thap Than - Uthumphon Phisai - Sisaket - Kanthararom - Warin Chamrap - Ubon Ratchathani
- Highway 2074: Buriram - Khu Mueang - Phutthaisong
Intercity transit
[edit]State Railway of Thailand (SRT), the national passenger rail system, provides service to Buriram at the Buriram Railway Station. SRT provides many services such as limited express trains to Bangkok and Ubon Ratchathani, commuter trains to Nakhon Ratchasima and beyond.
The Transport Co., Ltd. operates a bus depot at Buriram Bus Station, and Nakhonchai Air has its bus station adjacent.
Public transit
[edit]The Buriram Songthaew System (BSS) provides public transportation for the city. BSS was established many years ago. There are two lines: Line 1 (Buriram Municipality Market-Khao Kradong Forest Park Line), and Line 2 (Ban Bua Line). Both lines are colored pink.
Health
[edit]Buriram's main hospital is Buriram Hospital operated by the Ministry of Public Health.
Sports
[edit]Buriram promotes itself as a city of sport.[9] Buriram United is the most successful football team in Thailand after sweeping all before them by winning the league, the FA Cup, the League Cup, and AFC Champions League quarter-finalist.[citation needed] Buriram United play home games at Chang Arena, the largest club-owned football stadium in Thailand.[10]
A FIA Grade 1 and FIM Grade A racing circuit, Chang International Circuit, is near Chang Arena.
-
Chang Arena the largest club-owned football stadium in Thailand of Buriram United
Human achievement index 2022
[edit]| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 60 | 52 | 75 | 69 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |

|
 |

|
|
| 31 | 48 | 17 | 32 |
| Province Buriram, with an HAI 2022 value of 0.6136 is "low", occupies place 72 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[3]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 13 | "high" |
| 14 - 29 | "somewhat high" |
| 30 - 45 | "average" |
| 46 - 61 | "somewhat low" |
| 62 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2022 rankings |
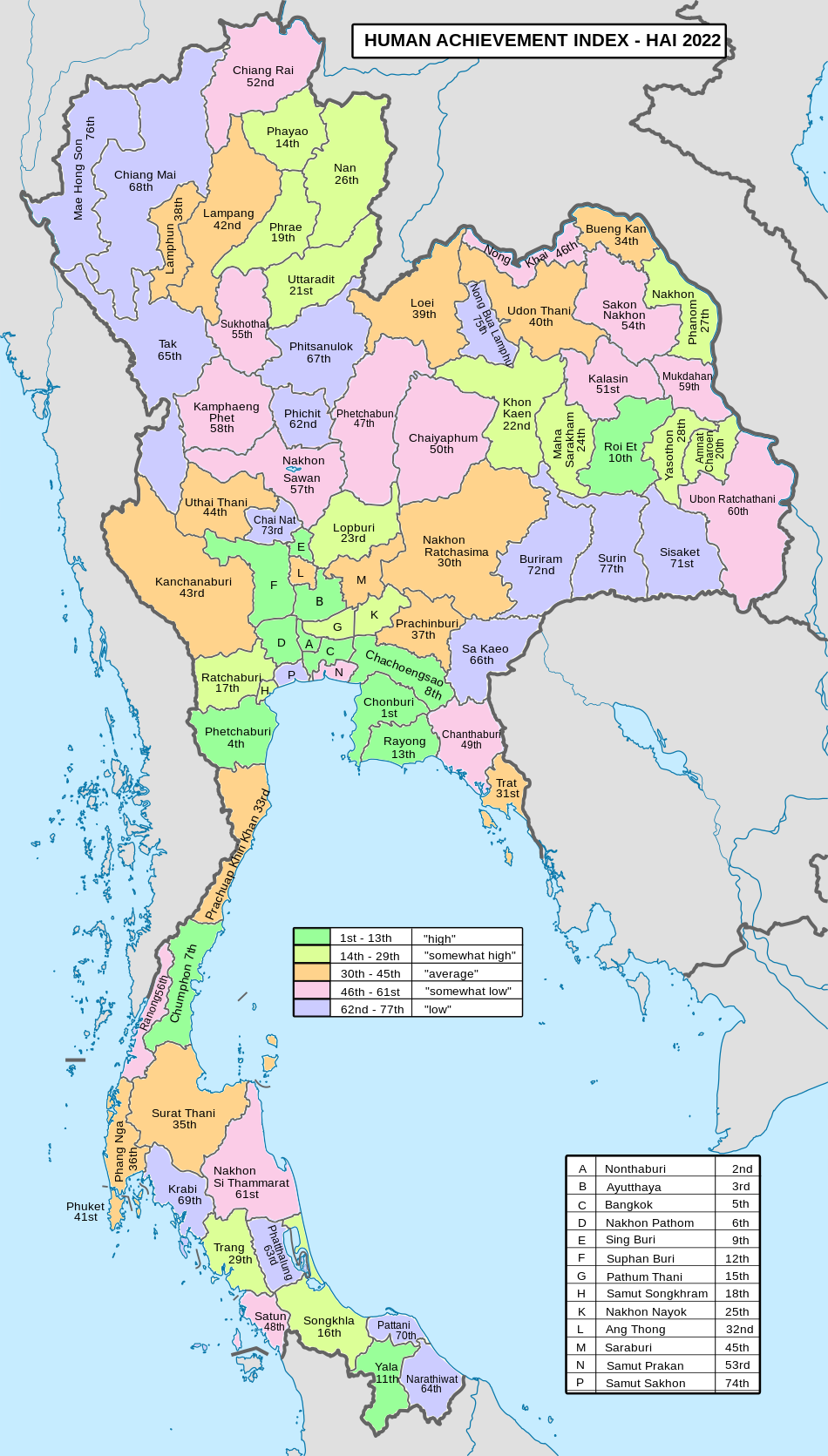
|
Notable people
[edit]
Born in Buriram
[edit]- Pira Sudham (พีระ สุธรรม) (born 1942), writer, author of Monsoon Country
- Newin Chidchob (เนวิน ชิดชอบ) (born 1958), politician, chairman of Buriram United
- Samransak Muangsurin (สำราญศักดิ์ เมืองสุรินทร์) (born 1959), former Muay Thai fighter
- Burklerk Pinsinchai (เบิกฤกษ์ ปิ่นสินชัย) (born 1966), former Muay Thai fighter
- Coban Lookchaomaesaitong (โคบาล ลูกเจ้าแม่ไทรทอง) (born 1966), former Muay Thai fighter
- Changpuek Kiatsongrit (ช้างเผือก เกียรติทรงฤทธิ์) (born 1966), former Muay Thai fighter
- Saencherng Pinsinchai (แสนเชิง ปิ่นสินชัย) (born 1967), former Muay Thai fighter
- Namphon Nongkeepahuyuth (นำพล หนองกี่พาหุยุทธ) (1969–2016), late Muay Thai fighter
- Therdkiat Sitthepitak (เทอดเกียรติ ศิษย์เทพพิทักษ์) (born 1970), former Muay Thai fighter
- Namkabuan Nongkeepahuyuth (นำขบวน หนองกี่พาหุยุทธ) (1973–2017), late Muay Thai fighter
- Samkor Chor.Rathchatasupak (สามกอ ช.รัชตสุภัค) (born 1975), former Muay Thai fighter
- Kompayak Porpramook (คมพยัคฆ์ ป.ประมุข) (born 1982), former professional boxer
- Sam-A Gaiyanghadao (สามเอ ไก่ย่างห้าดาว) (born 1983), former Muay Thai fighter and professional boxer
- Panomroonglek Kratingdaenggym (พนมรุ้งเล็ก กระทิงแดงยิม) (born 1984), former Muay Thai fighter and professional boxer
- Teerachai Sithmorseng (ถิรชัย ศิษย์หมอเส็ง) (born 1992), professional boxer
- Sasalak Haiprakhon (ศศลักษณ์ ไหประโคน) (born 1996), footballer
- Lalisa Manobal (ลลิษา มโนบาล) (born 1997), a member of the South Korean girl group Blackpink
- Chatchu-on Moksri (ชัชชุอร โมกศรี) (born 1999), volleyball player
References
[edit]- ^ a b "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019, Thailand boundary from Department of Provincial Administration in 2013
- ^ a b รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ส.2562 [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2019]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior. stat.bora.dopa.go.th (in Thai). 31 December 2019. Archived from the original on 14 June 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ a b "ข้อมูลสถิติดัชนีความก้าวหน้าของคน ปี 2565 (PDF)" [Human Achievement Index Databook year 2022 (PDF)]. Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC) (in Thai). Retrieved 12 March 2024, page 41
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "Gross Regional and Provincial Product, 2019 Edition". <>. Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council (NESDC). July 2019. ISSN 1686-0799. Retrieved 22 January 2020.
- ^ "ข้อมูลพื้นที่อุทยานแห่งชาติ ที่ประกาศในราชกิจจานุบกษา 133 แห่ง" [National Park Area Information published in the 133 Government Gazettes]. Department of National Parks, Wildlife and Plant Conservation (in Thai). December 2020. Archived from the original on 3 November 2022. Retrieved 1 November 2022.
- ^ "ตาราง 5 พื้นที่เขตรักษาพันธุ์สัตว์ป่า พ.ศ. 2562" [Table 5 Wildlife Sanctuary Areas in 2019] (PDF). Department of National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries and Plant Conservation (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 1 November 2022.
- ^ "Gregorian-Lunar Calendar Conversion Table". Hong Kong Observatory. Archived from the original on 3 November 2011. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
26 Buriram: 1 PAO, 3 Town mun., 59 Subdistrict mun., 146 SAO.
- ^ "บุรีรัมย์โมเดล ต้นแบบการสร้างเมืองใหม่".
- ^ "'บุรีรัมย์'กร้าวป้อง5แชมป์-ยึดท็อป5เอเชีย". Archived from the original on 2017-08-03. Retrieved 2017-08-03.
External links
[edit] Buriram travel guide from Wikivoyage
Buriram travel guide from Wikivoyage- Tourism Authority of Thailand: About Buriram[permanent dead link]
- Buriram Times
- Provincial website Archived 2020-08-06 at the Wayback Machine (Thai)
- Buriram provincial map, coat of arms and postal stamp[not specific enough to verify]











